Describe How Neurotransmitters Relay Messages From One Neuron to Another.
When new information is received by the first neuron it creates an electrical impulse that triggers the release of neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitters provide a chemical signal that links the nerve cells to one another.

What Is The Function Of The Synaptic Terminal Part Of The Neuron Socratic Neurons Anatomy And Physiology Physiology
Receptors receive and process the message then send it on to the next neuron.
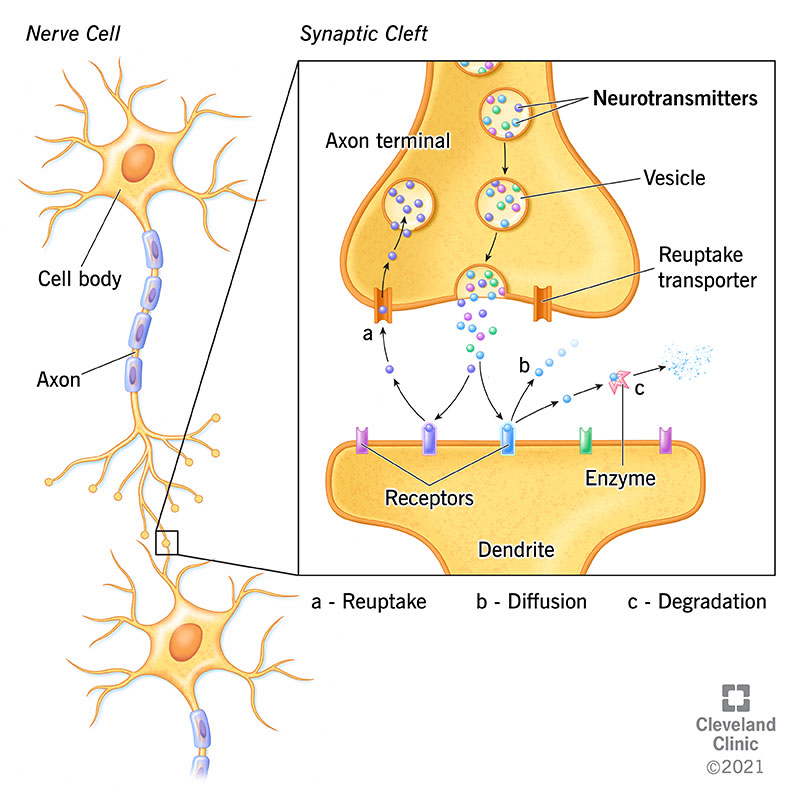
. It is within the space that a neurotransmitter is released. A synaptic connection between a neuron and a muscle cell is called a neuromuscular junction. Messages travel through neuron electrically using sodium potassium from the dendrites through the axon and out through axon terminal explain how a message travels from one neuron to another neuron neurotransmitters carry the message in them and send it to the next neuron - the neurons are separated by a synapse gap.
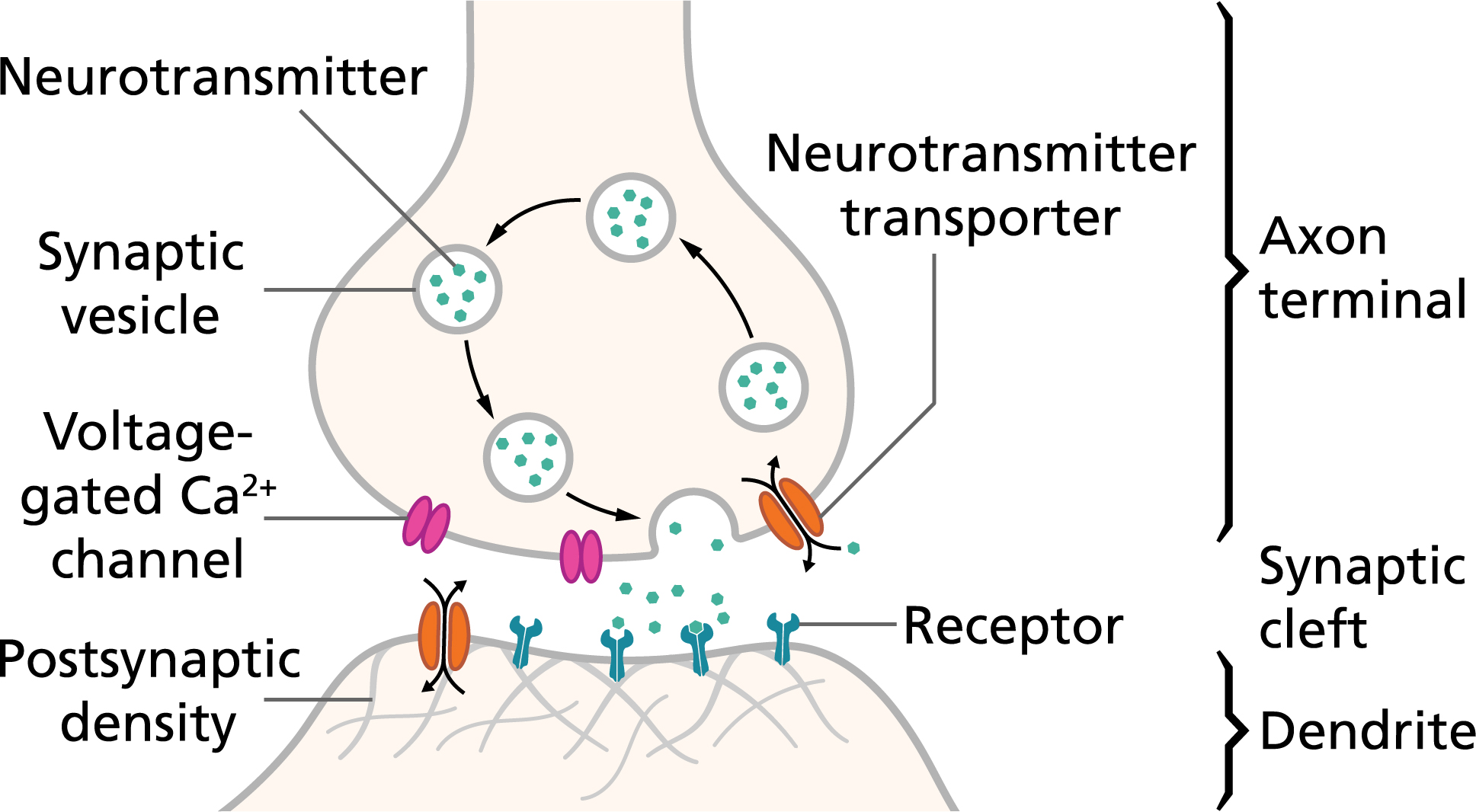
When an electrical signal reaches the end of a neuron it triggers the release of small sacs called vesicles that contain the neurotransmitters. Signals or information are passed over the synapse between neurons which allows information to travel throughout the nervous system. The transfer of information from neuron to neuron takes place through the release of chemical substances into the space between the axon and the dendrites.
Signals travel along the axon of a neuron which we will call neuron A in the form of an electrical impulse. Whether a neurotransmitter is excitatory or inhibitory depends on the receptor it binds to. A nerve impulse is transmitted from one neuron to another through junctions called synapses.
A neurotransmitter influences a neuron in one of three ways. The neurotransmitters then move across the gap to the second neuron where they bind to special molecules called receptors one for each kind of neurotransmitter. These chemicals are called neurotransmitters and the process is.
The neurotransmitter crosses the synapse and binds to a specialized site called a receptor on the other side. When neurons communicate the neurotransmitters from one neuron are released cross the synapse and attach themselves to special molecules in the next neuron called receptors. Neurotransmitters are molecules that travel from the synapses ofone neuron to the dendrites of another neuron activating channelson the second neuron that allow an influx of ions to rush in.
A synapse is formed by the membranes of a pre-synaptic neuron which may or may not be separated by a gap called synaptic cleft. Excitatory inhibitory or modulatory. How are messages passed from one neuron to another.
When neurons communicate an electrical impulse triggers the release of neurotransmitters from the axon into the synapse. The neurotransmitters cross the synapse and bind to. The neurotransmitter carries messages from.
When a neuron receives signals at the dendritesdue to neurotransmitters from an adjacent neuron binding to its receptorssmall pores or gates open on the neuronal membrane allowing Na ions propelled by both charge and concentration differences to move into the cell. There are two types of synapses namely electrical synapses and chemical synapses. Axon Hillock The dendrites send information through the cell body and then the cell integrates information at the.
The neurotransmitters then bind to receptors on the surface of neuron B. This gap is called a synapseit is so tiny that it is measured in nanometers or billionths of a meter. Each neurotransmitter binds only to its specific receptor just as a key fits only in a particular lock.
An excitatory transmitter promotes the generation of an electrical signal called an action potential in the receiving neuron while an inhibitory transmitter prevents it. With this influx of positive ions the internal charge of the cell becomes more positive. Typically a synapse is the space between the axon and the dendrite.
These sacs spill their contents into the synapse where the neurotransmitters then move across the gap toward the neighboring cells.
Action Potentials And Synapses Queensland Brain Institute University Of Queensland

Comments
Post a Comment